
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
L
Label - 1. An identifier within or attached to a set of data elements. 2. One or more characters that (a) are within or attached to a set of data elements and (b) represent information about the set, including its identification. 3. In communications, information within a message that is used to identify specific system parameters, such as the particular circuit with which the message is associated. Note: Messages that do not relate to call control should not contain a label. 4. In programming languages, an identifier that names a statement. 5. An identifier that indicates the sensitivity of the attached information. 6. For classified information, an identifier that indicates (a) the security level of the attached information or (b) the specific category in which the attached information belongs. 7. A field within a signaling message that contains information used to identify the circuit, call, or management transaction to which the message is related.
Label Bureau - A computer or server that supplies content labels or Web-site ratings. Synonym rating server.
Labeled Channel - In integrated services digital networks, (ISDN), a time-ordered set of all block payloads that have labels containing the same information, i.e., containing the same identifiers.
Labeled Interface Structure - In integrated services digital networks (ISDN), an interface structure that provides telecommunications services and signaling by means of labeled channels.
Labeled Multiplexing - In integrated services digital networks (ISDN), multiplexing by concatenation of the blocks of the channels that have different identifiers in their labels.
Labeled Statistical Channel - In integrated services digital networks (ISDN), a labeled channel in which the block payloads or the duration of each successive block is random.
Laboratory Attack - Use of sophisticated signal recovery equipment in a laboratory environment to recover information from data storage media.
Lambertian Radiator - See Lambertian source.
Lambertian Reflector - See Lambertian source.
Lambertian Source - An optical source that obeys Lambert's cosine law, i.e., that has an intensity directly proportional to the cosine of the angle from which it is viewed. Note: Conventional (surface-emitting) LEDs are approximately Lambertian. They have a large beam divergence. This results in a radiation pattern that resembles a sphere. Thus, most of their total optical output is not coupled into communication fibers.
Lambert's Cosine Law - See Lambertian source.
Lambert's Emission Law - Synonym Lambertian source.
LAN - Local Area Network. A data communications network that lies within a limited space (such as a building) to connect telephone lines, computers, modems, printers, etc.
LAN Application (software) - An application software package specifically designed to operate in a local-area-network environment.
Land Line - An informal name for conventional telephone facilities. Note: Land lines include conventional twisted-pair lines, carrier facilities, and microwave radio facilities for supporting a conventional telephone channel, but do not include satellite links or mobile telephone links using radio transmissions.
Land Mobile-Satellite Service - A mobile-satellite service in which mobile Earth stations are located on land.
Land Mobile Service - A mobile service between base stations and land mobile stations, or between land mobile stations.
Land Mobile Station - A mobile station in the land mobile service capable of surface movement within the geographical limits of a country or continent.
Landscape Mode - 1. In facsimile, the mode for scanning lines across the longer dimension of a rectangular object, i.e., rectangular original. 2. In computer graphics, the orientation of an image in which the longer dimension is horizontal. 3. An orientation of printed text on a page such that the lines of text are parallel to the long dimension of the page. Note: If the page contains an image, such as a picture, and the page is viewed in the normal manner, the long dimension of the page would be parallel to the line that joins the eyes of the viewer.
Land Station - A station in the mobile service not intended to be used while in motion.
Language - A set of characters, conventions, and rules that is used for conveying information.
Language Processor - A program that performs tasks, such as translating and interpreting, required for processing a specified programming language. Note: Examples of language processors include a Fortran processor and a COBOL processor.
LAN Operating System - See network operating system. - Software that (a) controls a Local Area network and its message (e.g., packet) traffic, and queues, (b) controls access by multiple users to network resources such as files, and (c) provides for certain administrative functions, including security.
LAP-B - The Data Link Layer protocol as specified by ITU-T Recommendation X.25 (1989).
LAP-D - Abbreviation for link access procedure D. A link protocol used in ISDN.
Large Prime Factors - Specially constructed large prime numbers, viz., p1, p2, q1, and q2, each > 2100, where p1 |p-1, p2 |p+1, q1|q-1, and q2 |q+1, where p and q are the private prime factors.
Laser - Acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. A device that produces a coherent beam of optical radiation by stimulating electronic, ionic, or molecular transitions to higher energy levels so that when they return to lower energy levels they emit energy. Note 1: Laser radiation may be either temporally coherent, spatially coherent, or both. Note 2: The degree of coherence of laser radiation exceeds 0.88.
Laser Chirp - An abrupt change of the center wavelength of a laser, caused by laser instability.
Laser Diode - Synonym injection laser diode. - A laser that uses a forward-biased semiconductor junction as the active medium. Note: Stimulated emission of coherent light occurs at a p-n junction where electrons and holes are driven into the junction.
Laser Disk - See optical disk. - A storage medium from which data is read and to which it is written by lasers. Optical disks can store much more data -- up to 6 gigabytes (6 billion bytes) -- than most portable magnetic media, such as floppies.
Laser Intelligence (LASINT) - Technical and geolocation intelligence derived from laser systems; a subcategory of electro-optical intelligence.
Laser Medium - Synonym active laser medium. - Within a laser, the material that emits coherent radiation or exhibits gain as the result of electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state or states, from a higher energy state or states to which it had been previously stimulated. Note: Examples of active laser media include certain crystals, gases, glasses, liquids, and semiconductors.
Lasing - See laser.
Lasing Threshold - The lowest excitation level at which laser output is dominated by stimulated emission rather than by spontaneous emission.
LASINT - Acronym for laser intelligence.
Last-In First-Out (LIFO) - A queuing discipline in which entities in a queue leave in the reverse order of the sequence in which they arrive. Note: Service, when available, is offered to the entity that has been in the LIFO queue the shortest time.
Last Number Redial - Synonym automatic redial. - A service feature that allows the user to dial, by depressing a single key or a few keys, the most recent telephone number dialed at that instrument. Note: Automatic redial is often associated with the telephone instrument, but may be provided by a PBX, or by the central office.
LATA - Acronym for local access and transport area. - Geographical boundaries within which local telephone companies may provide local telephone services (and some limited toll services). There are 184 LATAs in the United States.
Latency - The time it takes for a packet to travel from its point of origin to its point of destination. In telephony, the lower the latency, the better the communication. Latency has always been an issue with telephone communication taking place over exceptionally long distances (the United States to Europe, for example). With VoIP, however, latency takes on a new form because of the splitting of the message into packets (see packet-switched) and network delay in general.
Lateral Offset Loss - 1. In fiber optics, a loss of optical power at a splice or connector, caused by a lateral, i.e., transverse, offset of the mating fiber cores, which offset causes an imperfect transfer of the optical signal from the "transmitting" fiber to the "receiving" fiber. Note: The effect of a given amount of lateral offset will depend on other parameters such as the relative diameters of the respective cores. For example: if, because of manufacturing tolerances, the "transmitting" core is smaller than the "receiving" core, the effect will be less than if both cores were the same size. 2. An analogous loss of optical power caused by lateral misalignment of the fiber and optical source. Synonym transverse offset loss.
Launch Angle - 1. The angle, with respect to the normal, at which a light ray emerges from a surface. 2. The beam divergence at an emitting surface, such as that of a light-emitting diode (LED), laser, lens, prism, or optical fiber end face. 3. At an end face of an optical fiber, the angle between an input ray and the fiber axis. Note: If the end face of the fiber is perpendicular to the fiber axis, the launch angle is equal to the incidence angle when the ray is external to the fiber and the refraction angle when initially inside the fiber.
Launching Fiber - An optical fiber used in conjunction with a source to excite the modes of another fiber in a particular fashion. Note: Launching fibers are most often used in test systems to improve the precision of measurements. Synonym injection fiber.
Launch Numerical Aperture (LNA) - The numerical aperture of an optical system used to couple (launch) power into an optical fiber. Note 1: LNA may differ from the stated NA of a final focusing element if, for example, that element is underfilled or the focus is other than that for which the element is specified. Note 2: LNA is one of the parameters that determine the initial distribution of power among the modes of an optical fiber.
Layer - 1. In radio wave propagation, see F region. 2. In telecommunications networks and open systems architecture, a group of related functions that are performed in a given level in a hierarchy of groups of related functions. Note: In specifying the functions for a given layer, the assumption is made that the specified functions for the layers below are performed, except for the lowest layer.
Layered Protocol - The protocol reference model defined by layered structures based on and using the terminology of ITU-T Recommendations X.200 and X.210. The protocols referred to in this American National Standard conform to the OSI Reference Model for ISDN specified in ITU-T Recommendation I.320.
Layered System - A system in which components are grouped, i.e., layered, in a hierarchical arrangement, such that lower layers provide functions and services that support the functions and services of higher layers. Note: Systems of ever-increasing complexity and capability can be built by adding or changing the layers to improve overall system capability while using the components that are still in place.
Layer Entity - An active element within a layer.
Layer Function - A part of the activity of the layer entities.
Layer Interface - The boundary between two adjacent layers in the model.
Layer Service - A capability of the (N) layer and the layers beneath it, which is provided to (N + 1) layer entities, at the boundary between the (N) layer and the (N + 1) layer.
Layer Service Elements - An indivisible component of the layer service made visible to the service user via layer service primitives.
Layer Service Primitives - A means for specifying in detail the adjacent layer interactions
Layer User Data - Data transferred between corresponding entities on behalf of the upper layer or layer management entities for which they are providing services.
Lay Length - In communications cables--including fiber-optic cables--having the transmission media wrapped helically around a central member, the longitudinal distance along the cable required for one complete helical wrap; i.e., the total cable length divided by the total number of wraps. Note 1: In many fiber-optic cable designs, the lay length is shorter than in metallic cables of similar diameter, to avoid overstressing the fibers during the pulling associated with the installation operation. Note 2: The wraps, i.e., turns, that are referred to should not be confused with the twists given twisted metallic pairs, i.e., wires, to reduce electromagnetic coupling. Pairs of optical fibers are not given such twists. Synonym pitch.
LBO - Abbreviation for line buildout. Synonym building out. - The process of adding a combination of inductance, capacitance, and resistance to a cable pair so that its electrical length may be increased by a desired amount to control impedance and loss characteristics.
LCD - Abbreviation for liquid crystal display. - A display device that creates characters by means of the action of electrical signals on a matrix of liquid cells that become opaque when energized. Note: A liquid crystal display may be designed to be viewed by reflected or transmitted light.
LCD TV - Abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Display Television. LCD televisions are sets that use LCD technology to produce images. Benefits of LCD technology include lower weight and reduced power requirements when compared to other display types. Often, LCD television screens can also be used as computer monitors.
LCN- Abbreviation for Local Communication Network - A communication network within a TMN (telecommunications management network) that supports data communication functions (DCFs) normally at [specified] reference points q1 and q2. LCNs range from the simple to the complex. LCN examples include point-to-point connections and networks based on star and bus topologies.
LDAP - Abbreviation for lightweight directory access protocol. A simplified version of the X.500 standard, which version consists of a set of protocols developed for accessing information directories.
LDM - Abbreviation for limited distance modem.
Leaky Bucket Counter - A counter that is incremented by one each time an event occurs and is decremented by a fixed value periodically.
Leaky Mode - In an optical fiber, a mode having a field that decays monotonically for a finite distance in the transverse direction but becomes oscillatory everywhere beyond that finite distance. Note: Leaky modes correspond to leaky rays in the terminology of geometric optics. Leaky modes experience attenuation, even if the waveguide is perfect in every respect. Synonym tunneling mode.
Leaky Ray - In an optical fiber, a ray for which geometric optics would predict total internal reflection at the boundary between the core and the cladding, but which suffers loss by virtue of the curved core boundary. Note: Leaky rays correspond to leaky (i.e., tunneling) modes in the terminology of mode descriptors. Synonym tunneling ray.
Leap Second - An occasional adjustment of one second, added to, or subtracted from, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to bring it into approximate synchronism with UT1, which is the time scale based on the rotation of the Earth. Note 1: Adjustments, when required, are made with respect to the last second of the last minute of the day (Universal Time) on one of two annual days of opportunity (June 30 or December 31). Note 2: The last minute of the day on which an adjustment is made will therefore have 61 or 59 seconds. The former is the usual case, and the latter, a theoretical possibility if ever needed. Note 3: An adjustment is required on any day of opportunity when it is anticipated that if unadjusted, UTC will deviate from UT1 by more than 0.9 second before the next day of opportunity.
Leased Circuit - Dedicated common-carrier facilities and channel equipment used by a network to furnish exclusive private line service to a specific user or group of users.
Leased Line - A phone line dedicated for exclusive use from one location to another. High speed connections require a leased line.
Least Privilege - The principle requiring that each subject be granted the most restrictive set of privileges needed for the performance of authorized tasks. Application of this principle limits the damage that can result from accident, error, or unauthorized use of an information system (IS).
Least Significant Bit - In a binary code, the bit or bit position that is assigned to, or represents, the smallest quantity or increment that can be represented by the code.
Least-Time Principle - Synonym Fermat's principle. A principle stating that a ray of light follows the path that requires the least time to travel from one point to another, including reflections and refractions that may occur.
LEC - Abbreviation for local exchange carrier. - A local telephone company, i.e., a communications common carrier that provides ordinary local voice-grade telecommunications service under regulation within a specified service area.
LED - Abbreviation for light-emitting diode. - A semiconductor device that emits incoherent optical radiation when biased in the forward direction.
Left-Hand (anti-clockwise) Polarized Wave - An elliptically or circularly polarized wave, in which the electric field vector, observed in the fixed plane, normal to the direction of propagation, whilst looking in the direction of propagation, rotates with time in a left-hand or anticlockwise direction.
Leg - 1. A segment of an end-to-end route or path, such as a path from user to user via several networks and nodes within networks. Note: Examples of legs are several sequential microwave links between two switching centers and a transoceanic cable between two shore communications facilities, each connected to a node in a national network. 2. A connection from a specific node to an addressable entity, such as communication link from a computer workstation to a hub. 3. A loop termination of a multipoint circuit that links a bridge to the end user location.
Length Indicator (LI) - A six-bit field that defines message length and that is used to differentiate between message signal units, link status signal units, and fill-in signal units.
LEO - Abbreviation for low Earth orbit. A term used to describe the orbital altitude range (500 to 2000 km above the surface of the Earth) of certain communications satellites. Note 1: Generally, LEO satellites are part of constellations of satellites that achieve wide coverage of the Earth's surface with lower power requirements and shorter propagation delays than can be achieved with, e.g. Geostationary orbit satellites, or MEO satellites. Note 2: LEO satellites may have equatorial or polar paths. Note 3: Two LEO groups have emerged: Little LEO for data-communications satellites and Big LEO for data-and-voice communications, each using preassigned frequency ranges.
Letterbox - Letterbox is the term used when 16:9 content is viewed on a 4:3 screen. In order to display the widescreen content without distortion or missing parts of the picture, the television will place black bars at the top and bottom of the image.
Level - 1. The absolute or relative voltage, current, or power at a particular point in a circuit or system. 2. A tier or layer of a hierarchical system, e.g., the Link-Level protocol, high-level computer language.
Level Alignment - The adjustment of transmission levels of single links and of links in tandem to prevent problems such as overloading of transmission subsystems.
Level of Protection - The extent to which protective measures, techniques, and procedures must be applied to information systems (IS) and networks based on risk, threat, vulnerability, system interconnectivity considerations, and information assurance needs. Levels of protection are: 1. Basic: The IS and networks requiring implementation of standard minimum security countermeasures. 2. Medium: The IS and networks requiring layering of additional safeguards above the standard minimum security countermeasures. 3. High: The IS and networks requiring the most stringent protection and rigorous security countermeasures.
LF - Abbreviation for low frequency. - Any frequency in the band from 30 kHz to 300 kHz. See electromagnetic spectrum.
library - 1. An assembly of objects, routines, programs, etc., that may be drawn upon for use in the performance of functions. 2. Synonym forum.
Lifeline/Link-Up Program - A Federal program designed to provide telephone service to the poor and elderly at a reduced cost to assure they can be reached in case of an emergency.
LIFO: Acronym for last-in first-out. A queuing discipline in which entities in a queue leave in the reverse order of the sequence in which they arrive. Note: Service, when available, is offered to the entity that has been in the LIFO queue the shortest time.
Light - In a strict sense, the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be perceived by human vision, i.e., the visible spectrum, which is approximately the wavelength range of 0.4
m to 0.7
m. Note 1: In the laser and optical communications fields, custom and practice have extended usage of the term light to include the much broader portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be handled by the basic optical techniques used for the visible spectrum. Note 2: The region embraced by the term light has not been clearly defined, but by convention and usage, is considered to extend from the near-ultraviolet region of approximately 0.3
m, through the visible region, and into the mid-infrared region to approximately 30
m.
Light-Emitting Diode (LED) - A semiconductor device that emits incoherent optical radiation when biased in the forward direction.
Lightguide - See optical fiber.
Lightness - The brightness of an area subjectively judged relative to the brightness of a similarly illuminated area that appears to be white or highly transmitting.
Lightning Down-Conductor - In a lightning protection subsystem, the conductor connecting the air terminal or overhead ground wire to the earth electrode subsystem.
Lightning Protection Subsystem - All of the components used to protect a facility from the effects of lightning. Note: The lightning protection subsystem includes air terminals, lightning down- conductors, the earth electrode subsystem, air gaps, arresters, and their interconnections.
Light Pen - A stylus, usually hand-held, that contains a photodetector or light source, and that allows interaction with a computer through a specially designed monitor screen.
Light Valve - Synonym optical switch. - A switch that enables signals in optical fibers or integrated optical circuits (IOCs) to be selectively switched from one circuit to another. Note 1: An optical switch may operate by (a) mechanical means such as physically shifting an optical fiber to drive one or more alternative fibers, or (b) electro-optic effects, magneto-optic effects, or other methods. Note 2: Slow optical switches, such as those using moving fibers, may be used for alternate routing of an optical transmission path, e.g., routing around a fault. Fast optical switches, such as those using electro-optic or magneto-optic effects, may be used to perform logic operations.
Limited Protection - A form of short-term communications security applied to the electromagnetic or acoustic transmission of unclassified information that warrants a degree of protection against simple analysis and easy exploitation but that does not warrant protection to the extent needed for security of classified information.
Limited-Protection Voice Equipment - Equipment that provides limited security for unclassified voice communications.
Limiter - A device in which the voltage or some other characteristic of the output signal is automatically prevented from exceeding a specified value.
Limiter Circuit - A circuit of nonlinear elements that restricts the electrical excursion of a variable in accordance with specified criteria.
Limiting - Any process by which a specified characteristic (usually amplitude) of the output of a device is prevented from exceeding a predetermined value. Note 1: Hard limiting (" clipping ") is a limiting action in which there is (a) over the permitted dynamic range, negligible variation in the expected characteristic of the output signal, and (b) a steady-state signal, at the maximum permitted level, for the duration of each period when the output would otherwise be required to exceed the permitted dynamic range in order to correspond to the transfer function of the device. Note 2: Soft limiting is limiting in which the transfer function of a device is a function of its instantaneous or integrated output level. The output waveform is therefore distorted, but not clipped.
Limits of Interference - In radio transmission, the maximum permissible interference as specified in recommendations of the International Special Committee on Radio Interference or other recognized authority.
Line - 1. A physical medium for transferring electrical or electromagnetic energy from one point to another for purposes of communications. 2. A land line. 3. A metallic medium used for the transmission of electrical power. 4. A transmission medium, together with the associated equipment, required to provide the means of transporting information between two consecutive network elements, one of which originates the line signal and the other terminates the line signal. 5. Synonym scanning line.
Line Adapter Circuit - See four-wire terminating set. - A balanced transformer used to perform a conversion between 4-wire and 2-wire operation. Note 1: For example, a 4-wire circuit may, by means of a 4-wire terminating set, be connected to a 2-wire telephone set. Also, a pair of 4-wire terminating sets may be used to introduce an intermediate 4-wire loop into a 2-wire circuit, in which loop repeaters may be situated to amplify signals in each direction without positive feedback and oscillation. Note 2: Four-wire terminating sets have been largely supplanted by resistance hybrids.
Line Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) Code - The code generated by a regenerator upon loss of input signal or loss of frame. The line AIS signal will maintain operation of the downstream regenerators and therefore prevent generation of unnecessary alarms. At the same time, data and orderwire communication is retained between the regenerators and the downstream line terminating equipment
Linear Analog Control - Synonym linear analog synchronization. Synchronization in which the functional relationships used to obtain synchronization are of simple proportionality.
Linear Analog Synchronization - Synchronization in which the functional relationships used to obtain synchronization are of simple proportionality. Synonym linear analog control.
Linear Combiner - A diversity combiner in which the combining consists of simple addition of two or more signals.
Linear Device - A device for which the output is, within a given dynamic range, linearly proportional to the input.
Linearity - The property of a system in which, if input signals X and Y result in system output S (X) and S (Y) respectively, the input signal aX + bY will result in the output aS (X) + bS (Y), where S is the system transfer function and a and b are scalars.
Linear Key - In video technology and image processing, a process for the selective overlay of one video image upon another, as through chroma key. Note: Control of the ratio of foreground to background determined by the specifications derived from luminance information, and provided in the linear key data. Ratios to be applied are carried for each picture element in the alpha channel. The process permits realistic rendering of semi-transparent objects.
Linearly Polarized (LP) Mode - A mode for which the field components in the direction of propagation are small compared to components perpendicular to that direction. Note: The LP description is an approximation that is valid for a weakly guiding optical fiber, including typical telecommunications grade fibers.
Linear Network - See network topology. A network topology in which all nodes, i.e., stations, are connected together by a single bus.
Linear Optimization - In operations research, a procedure for locating the maximum or minimum of a linear function of variables that are subject to linear constraints. Synonym linear programming.
Linear Polarization - Of an electromagnetic wave, confinement of the E-field vector or H-field vector to a given plane. Note: Historically, the orientation of a polarized electromagnetic wave has been defined in the optical regime by the orientation of the electric vector, and in the radio regime, by the orientation of the magnetic vector. Synonym plane polarization.
Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) - A method of digitally encoding analog signals, which method uses a single-level or multilevel sampling system in which the value of the signal at each sample time is predicted to be a linear function of the past values of the quantized signal. Note: LPC is related to adaptive predictive coding (APC) in that both use adaptive predictors. However, LPC uses more prediction coefficients to permit use of a lower information bit rate than APC, and thus requires a more complex processor.
Linear Programming (LP) - In operations research, a procedure for locating the maximum or minimum of a linear function of variables that are subject to linear constraints. Synonym linear optimization.
Linear Topology -- See network topology. A network topology in which all nodes, i.e., stations, are connected together by a single bus.
Line Balance - The degree of electrical similarity of the two conductors of a transmission line. Note: A high degree of line balance reduces pickup of extraneous disturbances of all kinds, including crosstalk.
Line Buildout (LBO): Synonym building out. - The process of adding a combination of inductance, capacitance, and resistance to a cable pair so that its electrical length may be increased by a desired amount to control impedance and loss characteristics.
Line Code - A code chosen for use within a communications system for transmission purposes. Note 1: A line code may differ from the code generated at a user terminal, and thus may require translation. Note 2: A line code may, for example, reflect a requirement of the transmission medium, e.g., optical fiber versus shielded twisted pair.
Line Conditioning - The elimination of unintentional signals or noise induced or conducted on a telecommunications or information system signal, power, control, indicator, or other external interface line.
Line Conduction - Unintentional signals or noise induced or conducted on a telecommunications or information system signal, power, control, indicator, or other external interface line.
Line Driver - An amplifier used to enhance the transmission reliability of a usually digital intrafacility metallic transmission line, over extended distances, by driving the input to the transmission line with a higher than normal signal level. Note: An example of a line driver is an amplifier used to extend the range of an RS-232C digital signal beyond 50 feet (~15 m) while maintaining a specified bit-error ratio.
Line Filter Balance - A network designed to maintain phantom group balance when one side of the group is equipped with a carrier system. Note: Since it must balance the phantom group for only voice frequencies, the line filter balance configuration is usually simple compared with the filter that it balances.
Line Hit - See hit. - 1. A transient disturbance to, or momentary interruption of, a communication channel, power supply (especially that provided via a commercial electric power distribution network or grid, but not limited to same), etc.
Line Load Control - A network-provided service feature that allows selective denial of call origination to certain lines when excessive demands for service are required of a switching center.
Line Loop - See loop. - A pair of wires, or its equivalent, between a customer's station and the central office from which the station is served. Synonym user line.
Line Loopback - A signal used to command the far-end receiver to loopback the received line signal. ] Synonym [loosely] line loopback signal.
Line Loopback Signal - See line loopback.
Line Noise - In a telecommunications link or line facility, interference, from any source, that degrades performance. Note 1: Line noise is usually measured as a signal-to-noise ratio and as a set parameter used by engineers to determine the operating range of the system. Note 2: In analog lines, noise is usually measured in dbrnc (dB relative to -90 dBm, with C-message weighting). Note 3: In digital lines, noise is usually measured as a function of the number of errored bits per second or errors in the digital data stream. In digital systems with signal buffers, these errors may be linked to alarms, and to circuitry that enables the signal to be recovered to acceptable degree.
Line-Of-Sight (LOS) Propagation - Of an electromagnetic wave, propagation in which the direct ray from the transmitter to the receiver is unobstructed, i.e., the transmission path is not established by or dependent upon reflection or diffraction. Note: The need for LOS propagation is most critical at VHF and higher frequencies.
Line-Rate Conversion - A translation of standardized, existing video systems (using 525, 625, and 1125 total lines per frame) to proposed systems. Note: Current systems operate in a 2:1 interlace mode, i.e., with 262.5, 312.5, 562.5 lines per field and with concurrent temporal differences at field rates of 50.00, 59.94, or 60.00 fields per second. While simple transcoding by deletion or repetition can be applied, it is more commonly done by applying an algorithm to stored information in order to generate predictive line structures in the target system.
Line-Route Map - A map or overlay for signal communications operations that shows the actual routes and types of construction of wire circuits in the field. It also gives the locations of switchboards and telegraph stations.
Line Routing Switch - The Line Routing Switch 4.1 ™ is the newest line sharing technology in the world today. It does everything any fax switch on the market can do plus so much more at a lower cost. No longer do you have to compromise to save real money by reducing phone lines. Caller-id, Call waiting, and almost all of the phone company features are standard.
Line Routing Switch Pro - The Line Routing Switch Pro ™ is the very best industrial quality line sharing technology in the world. It has 5 ports ( for 4 dedicated phone devices plus an answering maschine if your application requires it) and does everything any industrial fax switch on the market can do including emergency barge-in as well as special modem polling features and so much more.
Line Routing Systems - The sole manufacturer's rep for the line sharing technology division of Long Range Systems. Line Routing Systems distributes all products and sales though local home town dealers.The local dealer will supply and advise the customer as necessary.
Line Routing Systems - www.lineroutingsystems.com
- LineShare Products - Line Routing Systems Products
- LRS LineShare 4.1- LineShare 4.1
- LRS LineShare Pro - LineShare Pro
- Line Routing Systems Dealer Login - Login or Create an Account
- About Line Routing Systems - About Us Line Routing Systems
- Line Routing Systems Customer Service - LRS Customer Service
- Line Routing Systems Privacy Policy - LRS Privacy Policy
- Line Routing Switches - Local Dealers - LRS Local Dealers
- Line Routing Switches Site Map - LRS Site Map
- Line Routing Switches Products Site Map - LRS Products Site Map
- Line Routing Systems Popular Search Terms - LRS Popular Search Terms
- Line Routing Systems Catalog Advanced Search - LRS Advanced Search
- Line Routing Systems Order Information - LRS Returns
- Line Routing Systems Contact Us - LRS Contact Us
Line Sharing - A technology that allows a single phone line to share incoming and outgoing access for multiple phone line connected devices. Typically Line Sharing Technology allows voice (phones and answering machine) and a fax machine or fax modem to operate on a shared phone line. Other applications include any variation of voice, a fax machine, fax/modem and/or modem(s).
Incoming calls are automatically routed to the proper device(s). If the call comes in and it is a fax call, the call is automatically routed to the fax machine or fax modem. If the call is a modem call, it is routed to the correct modem. Voice calls are routes to phone(s) and/or answering machine. May require a security access code (SAC) in the dialing string to automatically switch to the modem.
Since the need for to subscribe to a separate "fax line" from the local telephone company is eliminated, the return on investment (ROI) is very high. The initial cost of the device is returned in savings in a few months. After that you will save the monthly bills associated with fax, data or voice lines. For almost every business, line sharing technology is a smart investment.
LineShare 4.1- LineShare 4.1 ™ is the best new line sharing technology in the world today. This is perfect replacement for any Command Communications products. Almost every function that any switch that Commmand Communications ever made is included in this product plus more. It does everything any fax switch on the market can do plus so much more at a lower cost. Caller-id, Call waiting, and almost all of the phone company features are standard on the Lineshare 4.1.
LineShare Pro- LineShare Pro ™ is the telephone line management system that directs incoming phone calls to 1 of 4 destinations. It is capable of transferring calls in virtually many configurations of telephone devices.This is perfect replacement for any Command Communications products.
Almost every function that any switch that Commmand Communications or Multi-Link, Inc. product that was ever manufectured is included in this product plus much more. It does everything any fax switch on the market can do plus more. It supports up to 4 distinct phone connected devices plus an answering machine if voice is part of your application. Ir supports. Caller-id, Call waiting, and almost all of the phone company features are standard on the Lineshare Pro .
The LineShare Pro ™ does everything any fax switch on the market can do plus more. It supports up to 4 distinct phone connected devices plus an answering machine if voice is part of your application.
Line Side - The portion of a device that is connected to external, i.e., outside plant, facilities such as trunks, local loops, and channels.
Line Source - 1. In spectroscopy, an optical source that emits one or more spectrally narrow lines as opposed to a continuous spectrum. 2. In the geometric sense, an optical source having an emitting area in the form of a spatially narrow line, e.g., a slit. Synonym slit source.
Line Spectrum - In optics, an emission or absorption spectrum consisting of one or more narrow spectral lines, as opposed to a continuous spectrum.
Line Speed - See modulation rate. - The rate at which a carrier is varied to represent the information in a digital signal. Note: Modulation rate and information transfer rate are not necessarily the same.
Line Terminating Equipment (LTE): Network elements that originate and/or terminate line signals. LTEs can originate, access, modify, or terminate the transport overhead, or can perform any combination of these actions.
Line-to-Line Vorrelation - In facsimile, the correlation of object information from scanning line to scanning line. Note: Line-to-line correlation is used in two-dimensional encoding.
Line Traffic Coordinator (LTC): In a DDN switching center, the processor that controls traffic on a line.
Line Unit Network Termination (LUNT): The customer side of any digital subscriber line (DSL) that does not terminate on the customer installation.
Line Verification - See busy verification. - In a public switched telephone network, a network-provided service feature that permits an attendant to verify the busy or idle state of station lines and to break into the conversation. Note: A 440-Hz tone is applied to the line for 2 seconds, followed by a 0.5-second burst every 10 seconds, to alert both parties that the attendant is connected to the circuit.
Linewidth - See spectral width. - The wavelength interval over which the magnitude of all spectral components is equal to or greater than a specified fraction of the magnitude of the component having the maximum value. Note 1: In optical communications applications, the usual method of specifying spectral width is the full width at half maximum. This method may be difficult to apply when the spectrum has a complex shape. Another method of specifying spectral width is a special case of root-mean-square deviation where the independent variable is wavelength,
, and f (
) is a suitable radiometric quantity. Note 2: The relative spectral width ,
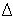
/
, is frequently used where
is obtained according to note 1, and
is the center wavelength.
Link - See Hypertext Link. 1. The communications facilities between adjacent nodes of a network. Synonym [loosely] telecommunications link. 2. A portion of a circuit connected in tandem with, i.e., in series with, other portions. 3. A radio path between two points, called a radio link. 4. In communications, a general term used to indicate the existence of communications facilities between two points. 5. A conceptual circuit, i.e., logical circuit, between two users of a network, that enables the users to communicate, even when different physical paths are used. Note 1: In all cases, the type of link, such as data link, downlink, duplex link, fiber optic link, line-of-sight link, point-to-point link, radio link and satellite link, should be identified. Note 2: A link may be simplex, half-duplex, or duplex. 6. In a computer program, a part, such as a single instruction or address, that passes control and parameters between separate portions of the program. 7. In hypertext, a logical connection between discrete units of data, or a hypertext connection between Web pages. Synonyms (in this sense) hotlink, hyperlink.Linkage - In computer security, the purposeful combining of data or information from one data processing system with data or information from another system to derive protected information. Synonym fusion.
Linked Registration - A type of AllCall registration feature, the use of which combines the registrations for incoming and outgoing calls for the current terminal address in a single procedure. However, unlike AllCall registration, a linked registration cannot be overridden in all or in part by: (a) InCall, remote InCall, AllCall, or remote AllCall registrations by the same UPT (Universal Personal Telecommunications service) user; (b) OutCall, remote OutCall, AllCall, remote AllCall, linked, or remote linked registrations by other UPT users. The UPT user must explicitly deregister a linked registration or override it by another linked or remote linked registration.
Link Encryption - 1. The application of on-line crypto-operation to a link of a communications system so that all information passing over the link is encrypted in its entirety. 2. Encryption of information between nodes of a communications system.
Linking Protection (LP) - In adaptive high-frequency (HF) radio, protection intended to prevent the establishment of unauthorized links or the unauthorized manipulation of legitimate links, and which are administered through an authorization process.
Link Layer - Deprecated term for Data Link Layer. Layer 2 of the Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model. This layer responds to service requests from the Network Layer and issues service requests to the Physical Layer. The Data Link Layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and to detect and possibly correct errors that may occur in the Physical Layer. Note: Examples of data link protocols are HDLC and ADCCP for point-to-point or packet-switched networks and LLC for local area networks. See Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model.
Link Level - In the hierarchical structure of a primary or secondary station, the conceptual level of control or data processing logic that controls the data link. Note: Link-level functions provide an interface between the station high-level logic and the data link. Link-level functions include (a) transmit bit injection and receive bit extraction, (b) address and control field interpretation, (c) command response generation, transmission and interpretation, and (d) frame check sequence computation and interpretation.
Link Orderwire - A voice or data communications circuit that (a) serves as a transmission link between adjacent communications facilities that are interconnected by a transmission link and (b) is used only for coordination and control of link activities, such as traffic monitoring and traffic control.
Link Protocol - A set of rules relating to data communications over a data link. Note: Link protocols define data link parameters, such as transmission code, transmission mode, control procedures, and recovery procedures.
Link Quality Analysis (LQA) - In adaptive high-frequency (HF) radio, the overall process by which measurements of signal quality are made, assessed, and analyzed. Note 1: In LQA, signal quality is determined by measuring, assessing, and analyzing link parameters, such as bit error ratio (BER), and the levels of the ratio of signal-plus-noise-plus-distortion to noise-plus-distortion (SINAD). Measurements are stored at--and exchanged between--stations, for use in making decisions about link establishment. Note 2: For adaptive HF radio, LQA is automatically performed and is usually based on analyses of pseudo-BERs and SINAD readings.
Link Set - A set of signaling links directly connecting two signaling points.
Link State Control - The control that coordinates functions of the signaling link, including signal unit delimitation, signal unit alignment, error detection, error correction, initial alignment, signaling link error monitoring, and flow control.
Link Status Signal Unit - A signal unit that contains status information about the signaling link in which it is transmitted.
Linux - A freeware version of the UnixTM operating system.
Lip Synchronization - The synchronization of audio and corresponding video signals so that there is no noticeable lack of simultaneity between them. Note: An example of a lip synchronization problem is the case in which television video and audio signals are transported via different facilities (e.g., a geosynchronous satellite link and a landline) that have significantly differently delay times, respectively. In such cases it is necessary to delay the audio electronically to allow for the difference in propagation times.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) - A display device that creates characters by means of the action of electrical signals on a matrix of liquid cells that become opaque when energized. Note: A liquid crystal display may be designed to be viewed by reflected or transmitted light.
List Address - In e-mail, an address used by mailing list subscribers to send e-mail to be distributed to each member of a discussion list, forum, interest group, mailing list, or newsgroup.
List Processor - Software used to manage and administer a discussion-group list, an interest group list, or a mailing list.
LISTSERV - Mailing lists that act as newsgroups.List Server - A functional unit (hardware and software) for operating a computer conferencing system by acting as a repository for electronic messages and redistributing those messages automatically or on-demand. Synonyms distribution list server, mailing list server.
Live Link - A link, on a World Wide Web file, that connects to another layer of information.
Livescript - See scripting language.
LLC - Abbreviation for logical link control. See logical link control sublayer. - In a local-area-network/metropolitan-area-network (LAN /MAN) system, the part of the link level that (a) supports medium-independent data link functions and (b) uses the services of the medium access control sublayer to provide services to the network layer.
LNA - Abbreviation for launch numerical aperture. - The numerical aperture of an optical system used to couple (launch) power into an optical fiber. Note 1: LNA may differ from the stated NA of a final focusing element if, for example, that element is underfilled or the focus is other than that for which the element is specified. Note 2: LNA is one of the parameters that determine the initial distribution of power among the modes of an optical fiber.
Load - 1. The power consumed by a device or circuit in performing its function. 2. A power-consuming device connected to a circuit. 3. To enter data or programs into storage or working registers. 4. To insert data values into a database that previously contained no occurrences of data. 5. To place a magnetic tape reel on a tape drive, or to place cards into the card hopper of a card punch or reader.
Load Capacity - In pulse-code modulation (PCM), the level of a sinusoidal signal that has positive and negative peaks that coincide with the positive and negative virtual decision values of the encoder. Note: Load capacity is usually expressed in dBm0. Synonym overload point.
Loader - A routine that reads data into main storage.
Load Factor - The ratio of the average load over a designated period of time to the peak load occurring during that period.
Loading - 1. The insertion of impedance into a circuit to change the characteristics of the circuit. 2. In multichannel communications systems, the insertion of white noise or equivalent dummy traffic at a specified level to simulate system traffic and thus enable analysis of system performance. 3. In telephone systems, the load, i.e., power level, imposed by the busy hour traffic. Note 1: The loading may be expressed as (a) the equivalent mean power and the peak power as a function of the number of voice channels or (b) the equivalent power of a multichannel complex or signal composite referred to zero transmission level point (0TLP). Note 2: Loading is a function of the number of channels and the specified voice channel mean power.
Loading Characteristic - In multichannel telephone systems, a plot, for the busy hour, of the equivalent mean power and the peak power as a function of the number of voice channels. Note: The equivalent power of a multichannel signal referred to the zero transmission level point is a function of the number of channels and has for its basis a specified voice channel mean power.
Loading Coil - A coil that does not provide coupling to any other circuit, but is inserted in a circuit to increase its inductance. Note 1: Loading coils inserted periodically in a pair of wires reduce the attenuation at the higher voice frequencies up to the cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter formed by (a) the inductance of the coils and distributed inductance of the wires, and (b) the distributed capacitance between the wires. Above the cutoff frequency, attenuation increases rapidly. Note 2: A common application of loading coils is to improve the voice-frequency amplitude response characteristics of twisted cable pairs. When connected across a twisted pair at regular intervals, loading coils, in concert with the distributed resistance and capacitance of the pair, form an audio-frequency filter that improves the high-frequency audio response of the pair. Note 3: When loading coils are in place, signal attenuation increases rapidly for frequencies above the audio cutoff frequency. Thus, when a pair is used to support applications that require higher frequencies, such as carrier systems, loading coils must be absent.
Load Sharing - A process used to route signaling traffic over two or more signaling routes for purposes of traffic equalization or security.
Lobe - 1. An identifiable segment of an antenna radiation pattern. Note: A lobe is characterized by a localized maximum bounded by identifiable nulls. 2. A pair of channels between a data station and a lobe attaching unit, one channel for sending and one for receiving, as seen from the point of view of the attached data station.
Lobe Attaching Unit - In a ring network, a functional unit used to connect and disconnect data stations to and from the ring without disrupting network operations.
Local Access and Transport Area (LATA) - Geographical boundaries within which local telephone companies may provide local telephone services (and some limited toll services). There are 184 LATAs in the United States. Under the terms of the Modification of Final Judgment (MFJ), a geographical area within which a divested Bell Operating Company (BOC) is permitted to offer exchange telecommunications and exchange access services. Note: Under the terms of the MFJ, the BOCs are generally prohibited from providing services that originate in one LATA and terminate in another.
Local Area Network (LAN) - A data communications system that (a) lies within a limited spatial area, (b) has a specific user group, (c) has a specific topology, and (d) is not a public switched telecommunications network, but may be connected to one. Note 1: LANs are usually restricted to relatively small areas, such as rooms, buildings, ships, and aircraft. Note 2: An interconnection of LANs within a limited geographical area, such as a military base, is commonly referred to as a campus area network. An interconnection of LANs over a city-wide geographical area is commonly called a metropolitan area network (MAN). An interconnection of LANs over large geographical areas, such as nationwide, is commonly called a wide area network (WAN).
Local Battery - 1. In telegraphy, the source of power that actuates the telegraphic station recording instruments, as distinguished from the source of power that furnishes current to the line. 2. In telephony, a system in which each telephone instrument has its own source of power, as opposed to being powered from the central office. 3. A source of local power for a telephone instrument.
Local call - 1. Any call using a single switching facility. 2. Any call for which an additional charge, i.e., toll charge, is not made to the calling or called party. Note: Calls such as those via "800" numbers do not qualify as local calls, because the called party is charged.
Local Central Office - Synonym central office. 1. A common carrier switching center in which trunks and/or loops are terminated and switched. Note: In the DOD, "common carrier" is called "commercial carrier." Synonym switch. Other synonyms [loosely] end office, exchange, local exchange, local office, switching center (except in DOD DSN [formerly AUTOVON] usage), switching exchange, telephone exchange. 2. A switching unit, in a telephone system which provides service to the general public, having the necessary equipment and operations arrangements for terminating and interconnecting subscriber lines and trunks or trunks only. There may be more than one central office in a building.
Local Channel - The portion of a private line circuit which is included in the exchange transmission plant. However, common usage of this term usually excludes information origination/termination equipment.
Local Clock - A source of timing located in close proximity to an associated facility, such as a communications station, central office, or node. Note: The same clock might be a remote clock relative to some other facility.
Local Communication Network (LCN) - A communication network within a TMN (telecommunications management network) that supports data communication functions (DCFs) normally at [specified] reference points q1 and q2. LCNs range from the simple to the complex. LCN examples include point-to-point connections and networks based on star and bus topologies.
Local Exchange - Synonym central office. In telephone communication in the United States, a local exchange office is an office in a locality to which subscriber home and business lines are connected on what is called a local loop. The local exchange has switching equipment that can switch calls locally or to long-distance carrier phone offices.
Local Exchange Carrier (LEC) - A local telephone company, i.e., a communications common carrier that provides ordinary local voice-grade telecommunications service under regulation within a specified service area.
Local Exchange Loop - An interconnection between customer premises equipment and telephone central office.
Local Line - See loop. A communications channel from a switching center or an individual message distribution point to the user terminal. Synonym subscriber line.
Local Loop - A pair of wires, or its equivalent, between a customer's station and the central office from which the station is served. Synonyms loop, user line.
Local Measured Service - See measured-rate service. - Telephone service for which charges are made in accordance with the total connection time of the line.
Local Node - A node which interfaces directly with customer equipment.
Local Number Portability Charge (LNP) - Allows a customer to keep the same phone number and "port" it over to another service provider. This is new to wireless. The terms number portability (NP) and local number portability (LNP) are often used interchangeably.
This charge may appear on the local portion of a phone bill if you live in an area where local number portability is provided. This fixed monthly charge allows local telephone companies to recover certain costs for providing “portability” to its customers. Local telephone companies may continue to assess this charge on their customers’ telephone bills for five years from the date the local telephone company first began itemizing the charge on the bill. This is not a tax.
Local Office - 1. Synonym central office. 2. A central office serving primarily as a place of termination for subscriber lines and for providing telephone service to the subscribers on these lines.
Local Orderwire - A communications circuit between a technical control facility and selected terminal or repeater locations within the communications complex. Note: In multichannel radio systems, the local orderwire is usually a handset connection at the radio location.
Local Reference - A local number, unambiguously identifying an SCCP (signaling connection control part) connection within one SCCP entity.
Local Side - The portion of a device that is connected to internal facilities, such as switches, patch panels, test bays and supervisory equipment.
Lock and Key Protection System - A protection system that involves matching a key or password with a specific access requirement.
Locked Mode - Synonym clock normal mode. - An operating condition of a clock in which the output signals are controlled by an external input reference. It is the expected mode. In normal mode, each clock in a chain has the same long-term average frequency, and the time error between the input and output of each clock is bounded. Only stratum 1 sources of timing require no input and therefore have a unique status of "normal" operation being equivalent to "freerun".
Lock-in Frequency - A frequency at which a closed-loop system can acquire and track a signal. See lock-in range.
Lock-in Range - 1. The range of frequencies within which a closed-loop system can acquire and track a signal. 2. The dynamic range within which a closed-loop system can acquire and track a signal.
Lockout - 1. In telephone systems, treatment of a user's line or trunk that is in trouble, or in a permanent off-hook condition, by automatically disconnecting the line from the switching equipment. 2. In public telephone systems, a process that denies an attendant or other users the ability to reenter an established connection. 3. In a telephone circuit controlled by two voice-operated devices, the inability of one or both users to get through, either because of excessive local circuit noise or because of continuous speech from either or both users. 4. In mobile communications, an arrangement of control circuits whereby only one receiver can feed the system at a time. Synonym receiver lockout system. 5. An arrangement for restricting access to use of all, or part of, a computer system. Synonym protection.
Log - Synonym journal. A chronological record of data processing operations that may be used to reconstruct a previous or an updated version of a file.
Logical Circuit - Synonym virtual circuit. A communications arrangement in which data from a source user may be passed to a destination user over various real circuit configurations during a single period of communication. Note: Virtual circuits are generally set up on a per-call basis and are disconnected when the call is terminated; however, a permanent virtual circuit can be established as an option to provide a dedicated link between two facilities.
Logical Link Control (LLC) Sublayer - In a local-area-network/metropolitan-area-network (LAN /MAN) system, the part of the link level that (a) supports medium-independent data link functions and (b) uses the services of the medium access control sublayer to provide services to the network layer.
Logical Route - Synonym virtual circuit. A communications arrangement in which data from a source user may be passed to a destination user over various real circuit configurations during a single period of communication. Note: Virtual circuits are generally set up on a per-call basis and are disconnected when the call is terminated; however, a permanent virtual circuit can be established as an option to provide a dedicated link between two facilities.
Logical Signaling Channel - A logical channel that provides a signaling path within an information channel or within a physical signaling channel.
Logical Topology - Of a network, the schematic configuration that reflects the network's function, use, or implementation without regard to the physical interconnection of network elements.
Logic Bomb - 1. Malicious logic that causes damage to a data processing system when triggered by some specific system condition. [2382-pt.8] 2. [A] resident computer program triggering an unauthorized act when particular states of an information system (IS) are realized.
Log In - To perform a login procedure. Synonym log on.
Login - The procedure that is followed by a user in beginning a session, e.g., a period of terminal operation. Synonym logon.
Login Name - The unique account name used to access a computer system. Also called user ID or user name, it is a way people identify themselves to their online service or Internet access provider.
Log Off - To perform a log-off procedure. Synonym log out.
Log-Off - The procedure that is followed by a user in closing a session, e.g., a period of terminal operation. Synonym log out.
Logon - Synonym login. The procedure that is followed by a user in beginning a session, e.g., a period of terminal operation.
Log On - Synonym log in. To perform a login procedure.
Log Out - Synonym log off. To perform a log-off procedure.
Log-Periodic (LP) Antenna - A broadband, multi-element, unidirectional, narrow-beam antenna that has impedance and radiation characteristics that are regularly repetitive as a logarithmic function of the excitation frequency. Note: The length and spacing of the elements of a log-periodic antenna increase logarithmically from one end to the other. Synonym log-periodic array.
Log-Periodic (LP) Array - Synonym log-periodic antenna. - A broadband, multi-element, unidirectional, narrow-beam antenna that has impedance and radiation characteristics that are regularly repetitive as a logarithmic function of the excitation frequency. Note: The length and spacing of the elements of a log-periodic antenna increase logarithmically from one end to the other.
Long-Distance Call - Any telephone call to a destination outside the local service area of the calling station, whether inter-LATA or intra-LATA, and for which there is a charge beyond that for basic service. Synonym toll call.
Long-Haul Communications - 1. In public switched networks, pertaining to circuits that span large distances, such as the circuits in inter-LATA, interstate, and international communications. 2. In the military community, communications among users on a national or worldwide basis. Note 1: Compared to tactical communications, long-haul communications are characterized by (a) higher levels of users, such as the National Command Authority, (b) more stringent performance requirements, such as higher quality circuits, (c) longer distances between users, including world wide distances, (d) higher traffic volumes and densities, (e) larger switches and trunk cross sections, and (f) fixed and recoverable assets. Note 2: "Long-haul communications" usually pertains to the U.S. Defense Communications System.
Longitudinal Balance - 1. The electrical symmetry, with respect to ground, of the two wires of a pair 2. An expression of the difference in impedance of the two sides of a circuit.
Longitudinal Offset Loss - Synonym gap loss. - 1. The power loss that occurs when an optical signal is transferred from one fiber to another that is axially aligned with it, but longitudinally separated from it. Note: The gap allows light from the "transmitting" fiber to spread out as it leaves the fiber endface. When it strikes the "receiving" fiber, some of the light will enter the cladding, where it is quickly lost. 2. An analogous form of coupling loss that occurs between an optical source, e.g., an LED, and an optical fiber. Note: Longitudinal Offset Loss is not usually significant at the optical detector, because the sensitive area of the detector is normally somewhat larger than the cross section of the fiber core. Unless the separation is substantial, all light emerging from the fiber, even though it diverges, will still strike the detector.
Longitudinal Redundancy Check (LRC) - A system of error control based on the formation of a block check following preset rules. Note 1: The block check formation rules are applied in the same manner to each character. Note 2: A combination of longitudinal and vertical redundancy check allows the detection and correction of single bit errors. Synonym horizontal redundancy check.
Longitudinal Voltage - A voltage induced or appearing along the length of a transmission medium. Note 1: Longitudinal voltage may be effectively eliminated by using differential amplifiers or receivers that respond only to voltage differences, e.g., those between the wires that constitute a pair. Note 2: Induced longitudinal voltages at low (power-line) frequencies can be greatly reduced by twisting parallel wires to create what are referred to as "twisted wire pairs."
Long Line - A transmission line in a long-distance communications network. Note: Examples of long lines are TDM and FDM carrier systems, microwave radio links, geosynchronous satellite links, underground cables, aerial cables and open wire, and submarine cables.
Long-Range Aid to Navigation (loran) System - See loran. A long-range radio navigation position-fixing system consisting of an array of fixed stations that transmit precisely synchronized signals to mobile receivers. Note: A loran receiver measures differences in the times of arrival of the signals from the various stations. A fixed difference in the time of arrival of the signals from any two stations will define a hyperbolic arc on which the receiver must lie. Three or more stations are needed to remove ambiguities in the position of the receiver.
Long-Range Radio Aid to Navigation System: See loran. A long-range radio navigation position-fixing system consisting of an array of fixed stations that transmit precisely synchronized signals to mobile receivers. Note: A loran receiver measures differences in the times of arrival of the signals from the various stations. A fixed difference in the time of arrival of the signals from any two stations will define a hyperbolic arc on which the receiver must lie. Three or more stations are needed to remove ambiguities in the position of the receiver.
Long-Term Bit Error Rate - Bit error rate measured over a sufficiently long period, for example, one month.
Long Silent Interval - A silent interval during a ringing cycle or pattern that lasts at least 1200 ms.
Long-Term Stability - Of an oscillator, the degree of uniformity of frequency over time, when the frequency is measured under identical environmental conditions, such as supply voltage, load, and temperature. Note: Long-term frequency changes are caused by changes in the oscillator elements that determine frequency, such as crystal drift, inductance changes, and capacitance changes.
Long Wavelength - In fiber optic communications, pertaining to optical wavelengths greater than
1
m.
Look-Ahead-For-Busy (LFB) Information - Information concerning network resources available to support higher precedence calls. Note 1: Available resources include idle circuits and circuits used for lower precedence calls. Note 2: LFB information may be used to make call-path reservations.
Loop - 1. A communications channel from a switching center or an individual message distribution point to the user terminal. Synonym subscriber line. 2. A pair of wires, or its equivalent, between a customer's station and the central office from which the station is served. Synonyms local loop, user line. 3. Go-and-return conductors of an electric circuit; a closed circuit. 4. A closed path under measurement in a resistance test. 5. A type of antenna, in the form of a circle or rectangle, usually used in direction-finding equipment and in UHF reception. 6. A sequence of instructions that may be executed iteratively while a certain condition prevails until the loop has been executed once.
Loop-Back - 1. A method of performing transmission tests of access lines from the serving switching center, which method usually does not require the assistance of personnel at the served terminal. 2. A method of testing between stations (not necessarily adjacent) wherein two lines are used, with the testing being done at one station and the two lines interconnected at the distant station. 3. A patch, applied manually or automatically, remotely or locally, that facilitates a loop-back test.
Loop Check - Synonym echo check. - A check to determine the integrity of transmission of data, whereby the received data are returned to the source for comparison with the originally transmitted data.
Loop Closure - A condition in which the network presents a low-resistance tip-to-ring dc path at the network interface (NI).
Loop Compensation Loss - The loss that could be provided by a digital loop carrier system or a fiber-in-the-loop system when a short customer analog access cable results in below-average attenuation.
Looped Dual Bus - A distributed-queue dual-bus (DQDB) scheme in which the head-of-bus functions for both buses are at the same location.
Loop Filter - In a phase-locked loop, a filter located between the phase detector (or time discriminator) and the voltage controlled oscillator (or phase shifter).
Loop Gain - 1. The total usable power gain of a carrier terminal or two-wire repeater. Note: The maximum usable gain is determined by, and may not exceed, the losses in the closed path. 2. The sum of the gains, expressed in dB, acting on a signal passing around a closed path, i.e., a loop.
Loophole - synonym flaw. In computer security, an error of commission, an omission, or an oversight that allows protection mechanisms to be bypassed or disabled.
Loop Noise - The noise contributed by one or both loops of a telephone circuit to the total circuit noise. Note: In a given case, it should be stated whether the loop noise is for one or both loops.
Loop Open - A signal in which the network applies a high resistance between the tip and ring conductors at the network interface (NI).
Loop Start - A supervisory signal given by a telephone or PBX in response to completing the loop path. A line or equipment that will establish a dial tone by completing a circuit between the two wires of the line. Automatic call processors, fax switches, all FAX machines and single-line phones, and most MODEMS are loop start equipment
Loop Test - A test that uses a closed circuit, i.e., loop, to detect and locate faults.
Loop Transmission - Multipoint transmission in which (a) all the stations in a network are serially connected in one closed loop, (b) there are no cross-connections, (c) the stations serve as regenerative repeaters, forwarding messages around the loop until they arrive at their destination stations, and (d) any station can introduce a message into the loop by interleaving it with other messages.
Loose Buffer - See buffer. - In a fiber optic communication cable, one type of component used to encapsulate one or more optical fibers for the purpose of providing such functions as mechanical isolation, protection from physical damage and fiber identification. Note: The buffer may take the form of a miniature conduit, contained within the cable and called a loose buffer, or loose buffer tube, in which one or more fibers may be enclosed, often with a lubricating gel. A tight buffer consists of a polymer coating in intimate contact with the primary coating applied to the fiber during manufacture.
Loran - Acronym for long-range radio navigation. A long-range radio navigation position-fixing system consisting of an array of fixed stations that transmit precisely synchronized signals to mobile receivers. Note: A loran receiver measures differences in the times of arrival of the signals from the various stations. A fixed difference in the time of arrival of the signals from any two stations will define a hyperbolic arc on which the receiver must lie. Three or more stations are needed to remove ambiguities in the position of the receiver. Synonyms long-range aid to navigation system, long-range radio aid to navigation system.
LOS - Abbreviation for line of sight. See line-of-sight propagation. - Of an electromagnetic wave, propagation in which the direct ray from the transmitter to the receiver is unobstructed, i.e., the transmission path is not established by or dependent upon reflection or diffraction. Note: The need for LOS propagation is most critical at VHF and higher frequencies.
Loss - 1. The diminution, usually expressed in dB, of signal level in a communications medium. 2. The power, usually expressed in watts, consumed or dissipated by a circuit or component without accomplishing useful work or purpose; e.g., heating (hysteresis loss) that occurs in the core of a transformer. 3. In computer security, a quantitative measure of harm or deprivation resulting from a compromise.
Lossless Compression - 1. In the storage of digital data, reduction, by the use of one or more appropriate algorithms, of the amount of data to be stored, in such a manner that the original data may be recovered precisely; i.e., in the exact original form. Note: The actual algorithm(s) applied to a given set of data may depend on the application (and hence, the statistical properties) of the data, e.g., for image storage. 2. An analogous real-time process applied to the transmission of digital data, with the objective of reducing the amount of data that need be transmitted per unit time; i.e., data rate, without compromising the ability to completely restore the data. 3. A digital image compression technique that allows for the removal of redundant bits without a resulting loss of image quality.
Lossy Compression - 1. In video and multimedia, bit-rate reduction of an image signal by powerful algorithms that compress beyond what is achievable in lossless compression or in quasi-lossless compression. Note: Lossy compression accepts loss of information and introduction of artifacts that can be ignored as unimportant when viewed in direct comparison with the original. Lossy compression takes advantage of the subtended viewing angle for the intended display, the perceptual characteristics of human vision, the statistics of image populations, and the objectives of the display. 2. In video technology, a digital image compression technique that removes redundant bits from an image in return for a minor loss of image quality.
Lossy Medium - A medium in which a significant amount of the energy of a propagating electromagnetic wave is absorbed per unit distance traveled by the wave.
Lost Block - A block not delivered to the user within a specified maximum end-to-end block transfer time.
Lost Call - A call that has not been completed for any reason other than cases where the call receiver (termination) is busy.
Lost Frame - A frame that is not delivered to the destination user within an agreed-upon measurement period, and the network is responsible. The procedure used to reach agreement on the measurement period should allow for the possibility that more than one network may be involved in the connection.
Low Earth Orbit - See LEO. A term used to describe the orbital altitude range (500 to 2000 km above the surface of the Earth) of certain communications satellites. Note 1: Generally, LEO satellites are part of constellations of satellites that achieve wide coverage of the Earth's surface with lower power requirements and shorter propagation delays than can be achieved with, e.g. Geostationary orbit satellites, or MEO satellites. Note 2: LEO satellites may have equatorial or polar paths. Note 3: Two LEO groups have emerged: Little LEO for data-communications satellites and Big LEO for data-and-voice communications, each using preassigned frequency ranges.
Lower Frequency Ground - Deprecated term. See facility grounding system. - The electrically interconnected system of conductors and conductive elements that (a) provides multiple current paths to the earth electrode subsystem, and (b) consists of the earth electrode subsystem, the lightning protection subsystem, and the fault protection subsystem.
Lowest Usable High Frequency (LUF) - The lowest frequency in the HF band at which the received field intensity is sufficient to provide the required signal-to-noise ratio for a specified time period, e.g., 0100 to 0200 UTC, on 90% of the undisturbed days of the month.
Low Frequency (LF) - Any frequency in the band from 30 kHz to 300 kHz. See electromagnetic spectrum.
Low-Level Keying - Synonym low-level signaling. - The use on signal lines of voltage levels that are between the limits of positive and negative 6 volts.
Low-Level Language - Synonym computer-oriented language. - A programming language in which words and syntax are designed for use on a specific computer or class of computers.
Low-Level Modulation - Modulation of a signal, e.g., a carrier, at a point in a system or device, such as a radio transmitter, where the power level is low compared to the final output power.
Low-Level Signaling - The use on signal lines of voltage levels that are between the limits of positive and negative 6 volts. Synonym low-level keying.
Low-Pass Filter - A filter network that passes all frequencies below a specified frequency with little or no loss, but strongly attenuates higher frequencies.
Low-Performance Equipment - 1. Equipment that has imprecise characteristics that do not meet system reliability requirements. 2. In military communications, equipment that has insufficiently exacting characteristics to permit its use in trunks or links. Note: Low-performance equipment may be used in loops if it meets loop performance requirements. 3. Tactical ground and airborne equipment that (a) has size, weight, and complexity characteristics that must be kept to a minimum and (b) is used in systems that have components with similar minimum performance characteristics.
Low-Power Communication Device - A restricted radiation device, exclusive of those employing conducted or guided radio frequency techniques, used for the transmission of signs, signals (including control signals), writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by radiation of electromagnetic energy. Examples: Wireless microphone, phonograph oscillator, radio-controlled garage door opener, and radio-controlled models.
Low-Power FM Radio (LPFM) - A broadcast service that permits the licensing of 50- to 100-watt FM radio stations within a service radius of up to 3.5 miles and 1- to 10-watt FM radio stations within a service radius of 1 to 2 miles.
Low-Power Television (LPTV) - A broadcast service that permits program broadcasting via television translators operating with low power. LPTV service includes the existing translator service and operates on a secondary basis to regular television stations. Transmitter output is limited to 1,000 watts for normal VHF stations and 100 watts when a VHF operation is on an allocated channel.
LP - Abbreviation for linear programming, linking protection.
L-pad - A pad composed of two discrete components, one series component and one shunt component. Note: In schematic representation, the components resemble the upper-case letter "L," hence the name.
LPC - Abbreviation for linear predictive coding. - A method of digitally encoding analog signals, which method uses a single-level or multilevel sampling system in which the value of the signal at each sample time is predicted to be a linear function of the past values of the quantized signal. Note: LPC is related to adaptive predictive coding (APC) in that both use adaptive predictors. However, LPC uses more prediction coefficients to permit use of a lower information bit rate than APC, and thus requires a more complex processor.
LP Mode - Abbreviation for linearly polarized mode. - A mode for which the field components in the direction of propagation are small compared to components perpendicular to that direction. Note: The LP description is an approximation that is valid for a weakly guiding optical fiber, including typical telecommunications grade fibers.
LP01 mode - Designation of the fundamental LP mode. See fundamental mode.
LPTV - Abbreviation for Low-Power TV. These are TV stations who are locally-oriented broadcasters -- operated by high schools/colleges, churches/religious groups, local governments, small/large businesses and individual citizens. There is currently no deadline for these categories of stations to convert to digital broadcasting
LQA - Abbreviation for link quality analysis. - In adaptive high-frequency (HF) radio, the overall process by which measurements of signal quality are made, assessed, and analyzed. Note 1: In LQA, signal quality is determined by measuring, assessing, and analyzing link parameters, such as bit error ratio (BER), and the levels of the ratio of signal-plus-noise-plus-distortion to noise-plus-distortion (SINAD). Measurements are stored at--and exchanged between--stations, for use in making decisions about link establishment. Note 2: For adaptive HF radio, LQA is automatically performed and is usually based on analyses of pseudo-BERs and SINAD readings.
LRC Abbreviation for longitudinal redundancy check. - A system of error control based on the formation of a block check following preset rules. Note 1: The block check formation rules are applied in the same manner to each character. Note 2: A combination of longitudinal and vertical redundancy check allows the detection and correction of single bit errors.
LSB - Abbreviation for least significant bit, lower sideband.
LTC - Abbreviation for Line Traffic Coordinator - In a DDN switching center, the processor that controls traffic on a line.
.l3 - A file-name extension that identifies a Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG) audio file. [Bahorsky]
LTE - Abbreviation for Line Terminating Equipment - Network elements that originate and/or terminate line signals. LTEs can originate, access, modify, or terminate the transport overhead, or can perform any combination of these actions.
LUF - Acronym for lowest usable high frequency. - The lowest frequency in the HF band at which the received field intensity is sufficient to provide the required signal-to-noise ratio for a specified time period, e.g., 0100 to 0200 UTC, on 90% of the undisturbed days of the month.
Luminance Range - 1. In CRT displays, the difference in brightness between the lightest and the darkest element of a scene or its display. 2. Of a CRT or other display device, the ratio of (a) the maximum brightness that is (or can be) displayed to (b) the minimum brightness that is (or can be) displayed.
Luminance Signal - 1. In television technology, the signal that describes (a) the distribution of brightness levels within the image and (b) the equation for deriving that information from the camera output. 2. In composite color television, a signal that has major control of the brightness. Note: Luminance signal is a linear combination of gamma-corrected primary color signals.
Luminescent Diode - See superluminescent LED. - A light-emitting diode in which there is stimulated emission with amplification but insufficient feedback for oscillations to build up to achieve lasing action.
Luminous Flux - The rate of flow of radiant energy. Note: Luminous flux is expressed in lumens
Luminous Intensity - See candela. - The luminous intensity in a specified direction, of a monochromatic source which has a frequency of 540 x 1012 Hz and which has a radiant intensity, in the specified direction, of (1/683) watt per steradian.
LUNT - Abbreviation for Line Unit Network Termination - The customer side of any digital subscriber line (DSL) that does not terminate on the customer installation.
Lurker - In the Internet, a participant in a chat room or a subscriber to a mailing list or newsgroup who passively observes but does not actively participate in the exchange.
Lurking - Passive participation in (i.e., monitoring) the activities of a mailing list, a newsgroup, an IRC channel, a video connection, or any other Internet communication device. Note: Lurking is generally carried out for the purpose of nondirected information gathering or to allow a new user to first understand the focus and the manners of a discussion group.
Lynx - A World Wide Web browser that provides a character-based user interface to hypertext-based information. Note: Lynx can display only character-based portions of the hypertext-based information.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
You didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock from over 200 premier manufacturers.